Deforestation
What Causes Deforestation?
Forests and ecosystems are being destroyed for timber harvesting, agriculture, shifting population, cattle ranching and firewood collection.
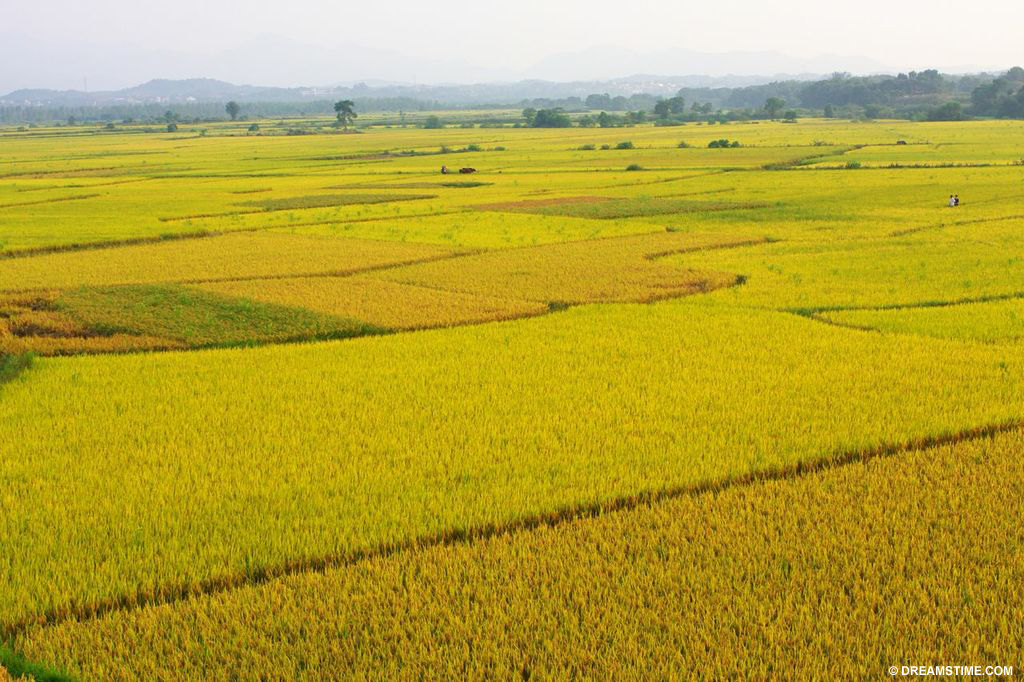

Agriculture is responsible for 80% of global deforestation
Wood-hungry Populations
Logging is the number one cause of forest degradation. It is estimated that more than 5,000 food and wood products that we use come from our forests. Trees are removed from forests either through selective, strip or clear-cutting methods for our lumber and paper products. Roughly 4 billion trees – or 35 percent of the trees – cut around the world are for our paper industries.
We can’t ignore the worldwide ecological necessity of our forests and trees, because we believe we are dependent on wood and paper products. Seventy percent of forest degradation in Latin America and subtropical Asia is caused by logging[4. Gabrielle Kissinger, Martin Herold and Veronique De Sy. Drivers of Deforestation and Degradation. August 2012.]. In Indonesia, logging operations destroyed about 40 percent of the trees left behind. In many third world countries, logging operations have lead to a permanent loss of forest.[5. What are the Major Causes of Deforestation? http://www.preservearticles.com/]
Canada is the second largest exporter of primary forest products in the world – the US is the first[6. Natural Resources Canada. “Canada’s Forest Industry: An overview.” 2012.]. Clear cutting is not considered deforestation if trees are replanted, or if allowed to regenerate naturally they aren’t included in international statistics[7. Natural Resources Canada. Deforestation in Canada: The Facts? Jan. 15, 2013.]. From 2000 to 2005, the greatest loss to deforestation worldwide happened in the boreal forests in places like North America.[8. Science 2.0 “Study Tracks Worldwide Forest Loss, Boreal See Greatest Decline.” May 7, 2010.]
Fire!

Fire is used as a tool to clear forested land for agriculture, mining, roads, homes and other uses
Fire is used to clear forested land for trees and vegetation, for agriculture, mining, roads and homes. These fires not only kill our trees, they release carbon stored by the trees as carbon dioxide into the air. Forest fires increase climate change and ocean acidification. We also lose their future ability to absorb carbon and create oxygen.
Natural fires also take their toll on our forests. Experts are warning that dry conditions caused by global warming, droughts and El Niños are an increasing danger for forest fires worldwide.
Record-breaking temperatures in Australia in the summer of 2012 led to massive forest fires: 141 fires raged simultaneously, in one day, and 1,300 square kilometres of forest and farmland were lost. These enormous fires could be seen from the International Space Station.[9. New York Times. January 9, 2013. Record Heat Fuels Widespread Fires in Australia. www.nytimes.com]
Climate change, ocean acidification and deforestation are environmental issues that not only need our immediate attention they also are intertwined and impact one another. We must look at all environmental threats to make a difference.
Illegal Logging
Illegal logging is the taking of more trees than allowed, harvesting protected species and taking trees from protected forests.
In some developing countries, 50 percent of illegal logging occurs because they are using trees for heating and cooking. There obviously needs to be replanting and alternatives for people using their local trees for daily life. Of course, the wood industry is also to blame for illegal logging: 48 percent of the timber from Mozambique’s forests supplied to Chinese companies in 2012 was harvested illegally.[10. Jeremy Hance. “Report: nearly half the timeber from Mozambieque to China is illegal.” Feb. 7, 2013. mongabay.com]
What is the Danger of Illegal Logging?
The environment, local peoples and the forestry industry suffer when trees are cut down without replanting or trees are cut down faster than forests can recover. We must put a stop to illegal logging, protect, sustainably manage our forests and replant trees. Logging can be done responsibly and our trees can be preserved.
It is important that the frontier forests remain untouched. The ecological and evolutionary processes of our frontier forests maintain diversity that makes our planet habitable – such as watershed protection and climate stabilization. Also these forests are home to many of the world’s indigenous peoples.
Cutting Down Trees for Meat and Crops
Meat consumption is a big cause of deforestation. Seventeen percent of the Amazon forest was lost in the past 50 years to cattle ranches.[11. World Wildlife Fund. www.worldwildlife.org]
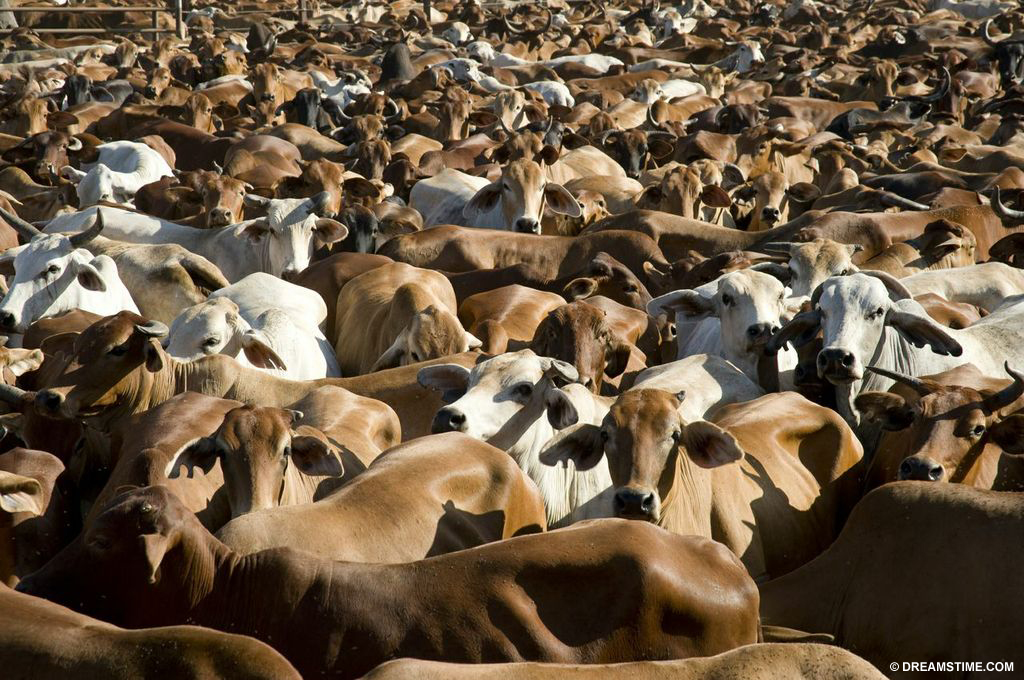

Cattle ranch
In tropical areas, agriculture consumes the land. Farmland is therefore responsible for 80 percent of global deforestation. Corporations and local farmers take over forests and clear the trees for cattle ranching and high-demand crops such as soybeans and palm oils, and land is cleared for small family farms. Farmers clear the land by burning the forests or cutting down trees. Livestock and agriculture farming is responsible for roughly 95 percent of deforestation in Latin America, 75 percent in Africa and 70 percent in subtropical Asia.[12. Gabrielle Kissinger, Martin Herold and Veronique De Sy. Drivers of Deforestation and Degradation. August 2012.]
Palm Oil and Soybeans
In 2006, global production of soybeans and palm oil reached record levels[13. United Nations Environment Programme. Vital Forest Graphics. 2009]. In many countries, like Brazil and Southeast Asia, commercial agriculture is the cause of more deforestation than family farming.
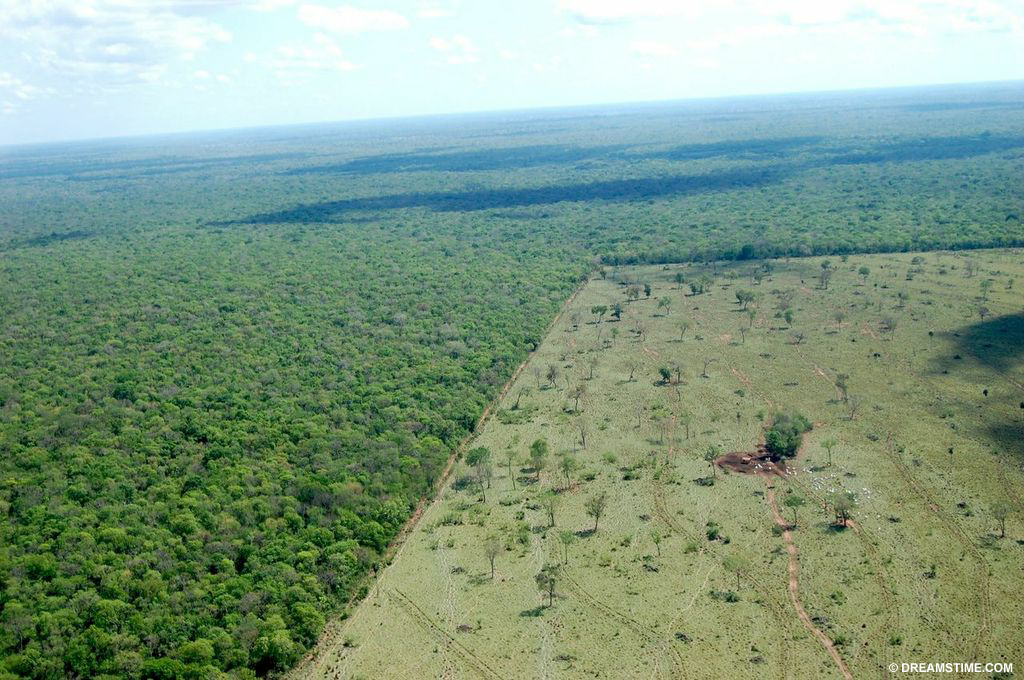

Deforestation in Amazon, Brazil
Palm Oil: It’s used in everything!
Palm oil is one of the most versatile raw materials in the world. You can find it in everything from margarine, cereals and baked goods to washing powders, soaps and cosmetics. You may have never heard of it because usually it is listed as ‘vegetable oil’ in the ingredients list. [14. Green Palm Sustainability, Palm Oil Products]Palm oil can also be used in animal food and biofuel.
The worldwide demand for palm oil is expected to double between 2000 and 2020.
Already 60 percent of international trade is in vegetable oils.[15. UNEP Global Environmental Alert Service. “Oil palm plantations: threats and opportunities for tropical ecosystems. December 2011.” www.unep.org] Malaysia and Indonesia are responsible for 90 percent of palm oil production. Indonesia has 6 million hectares of oil palms—and has already lost 72 percent of their forests.[16. Greenpeace UK. “Palm Oil.” www.greenpeace.org.uk] Ironically, the expansion of palm oil plantations in Indonesia and Malaysia is a response to high petroleum prices and an increasing global demand for soybean-based biofuels perceived to be ‘green.’[17. NASA. http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov] As consumers, it is always important to be armed with as much information as possible to make truly environmentally sound decisions.
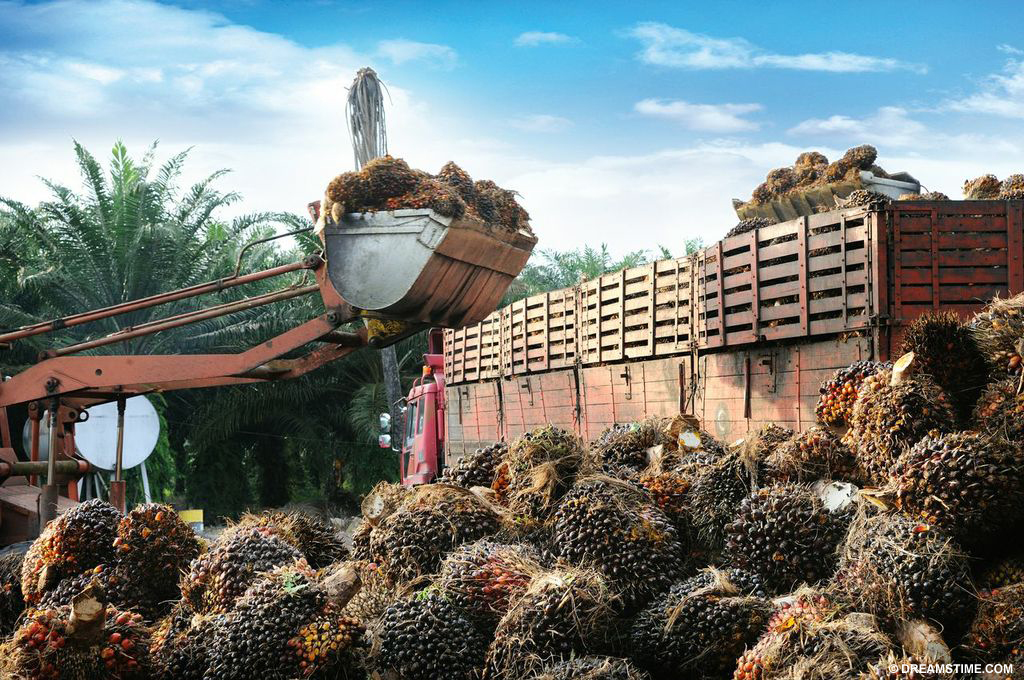

In 2006, global production of soybeans and palm oil reached record levels.
Palm oil plantations are not only destroying forests. They are impacting and displacing species, such as Asian elephants, orangutans, Sumatran rhinoceros, tigers and proboscis monkeys, all of which are endangered or critically endangered.
Soybean Crop: Livestock and Plastics
Most of the world’s soy crop is used for livestock feed; soybean meal is the largest source of protein feed in the world.[18. World Wildlife Fund International. www.panda.org] Soybean crops, like palm oil plantations are very versatile. Soybeans are used in numerous high demand products and food like: tofu, biodiesel, vegetable oil, paint and plastic.
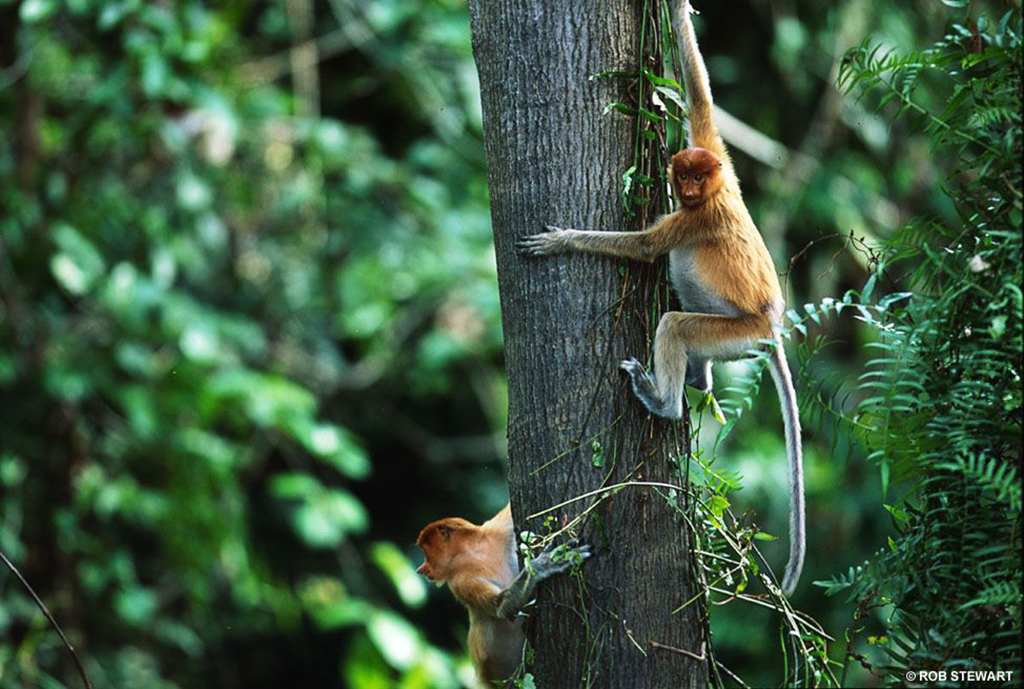

Living only in the forests of Borneo, proboscis monkeys are endangered due to deforestation
Brazil, Argentina, China and India have all become major producers of soybean crops. Brazil as the world’s second biggest soybean supplier produces 23 percent of the global total and is expected to rise to number one.[19. United Nations Environment Programme. Vital Forest Graphics. 2009. unep.org/vitalforest] As the demand for soybeans increases, Brazil clears more forestland for soybean crops – even cattle are being displaced as soybeans in Brazil take over ranch land.[20. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. “Sustainable development and challenging deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon: the good , the bad and the ugly. 2007. www.fao.org]
The rapid increase of soybean crops in Brazil is also leading to the displacement of the manned wolf and giant anteater.[21. World Wildlife Fund International. www.panda.org]
Agriculture is Destroying our Forests
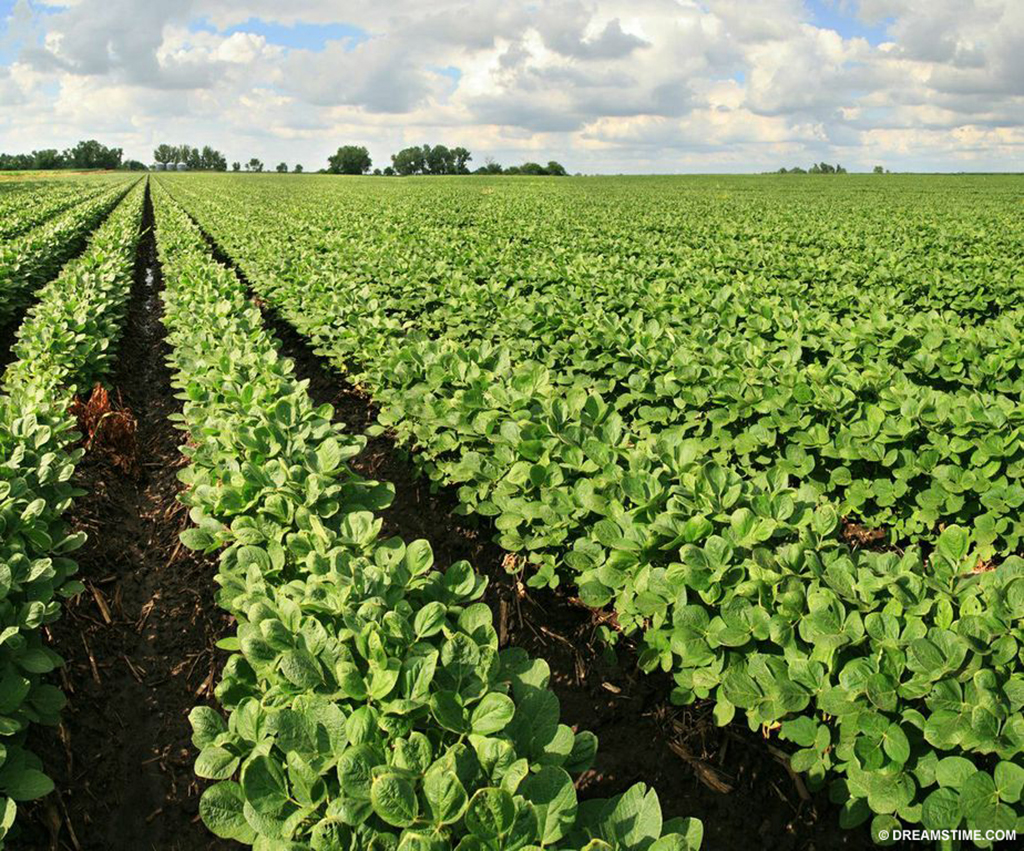

Soybean crops
Currently 11 percent – 1.5 billion hectares – of the Earth’s land is used to grow crops.[22. FAO. World Agriculture: Towards 2015/2030. An FAO perspective… www.fao.org] This amount is going to increase as populations develop, meat-based diets increase and international markets grow. Our global population is expected to increase to 8.2 billion by 2030. The demand for meat is expected to increase by 85 percent by 2050 and 78 percent of the meat will come from developing countries.[24. Gabrielle Kissinger, Martin Herold and Veronique De Sy. Drivers of Deforestation and Degradation. August 2012.]
There is going to be an increase to 120 million hectares of cropland by 2030.[23. Gabrielle Kissinger, Martin Herold and Veronique De Sy. Drivers of Deforestation and Degradation. August 2012.] The bulk of this growth is going to take place in sub-Saharan Africa, with 60 million hectares, Latin America with 41 million hectares and East Asia, excluding China with 14 million. We still don’t know how much of the 120 million hectares will come from forests. There is still time to impact how, and what land, is being used for agriculture.
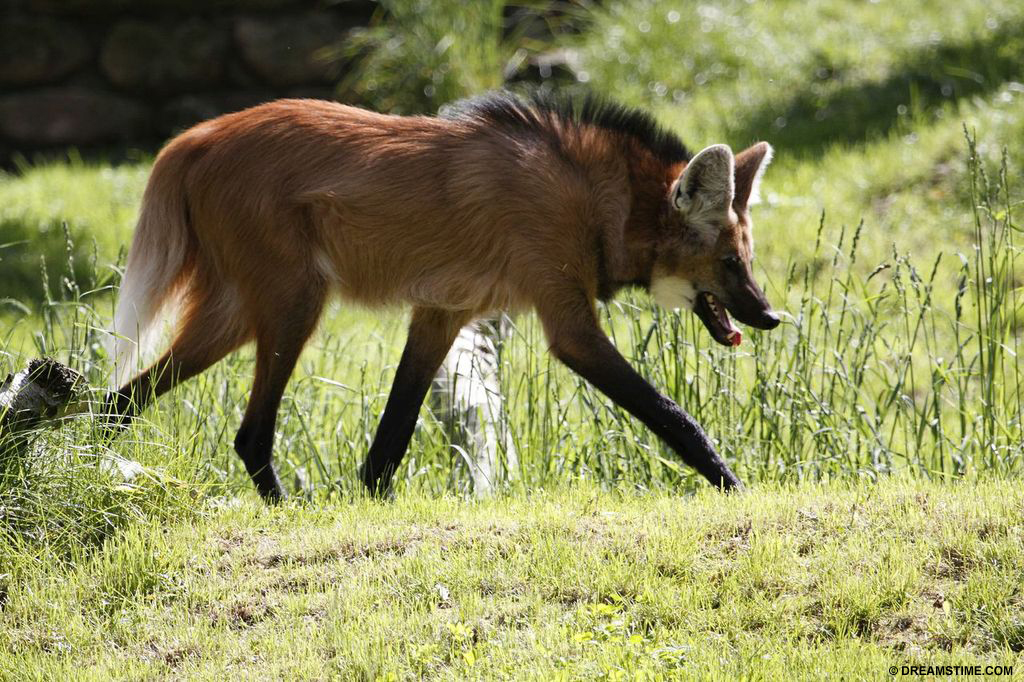

Species affected by soybean crops include the maned wolf and giant anteater in Brazil